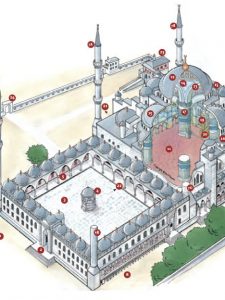
Sultan Ahmed Mosque
The Sultan Ahmed Mosque, commonly known as the Blue Mosque, is one of the most iconic landmarks in Istanbul, Turkey. It is renowned for its stunning architecture, intricate tilework, and its prominent position within the city’s skyline.
Sultan Ahmed Mosque (Blue Mosque) in Istanbul
A user friendly and informative Pamphlet with illustrations and plans. Its content is very easy to understand. In addition to general information about the Sultan Ahmed Mosque (Blue Mosque) in Istanbul, Turkey, it shows the photos of all of the major monuments in and around the mosque. A general plan of the surrounding areas will help the reader to get oriented to the Sultanahmet neighborhood.
Buy Sultan Ahmed Mosque Pamphlet
ISBN: 978-605-60629-7-1 Quick Guide Sultan Ahmed Mosque (English, Turkish, German, French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Greek, Arabic)
Available at Museum Shops in Turkey
Here are some key facts about the Blue Mosque:
 Name and Nickname: The mosque is officially called the Blue Mosque, named after Sultan Ahmed I, who commissioned its construction. However, it is more commonly known as the Blue Mosque due to the blue tiles that adorn its interior.
Name and Nickname: The mosque is officially called the Blue Mosque, named after Sultan Ahmed I, who commissioned its construction. However, it is more commonly known as the Blue Mosque due to the blue tiles that adorn its interior.- Commission and Construction: Sultan Ahmed I ordered the construction of the mosque in the early 17th century. The construction began in 1609 and was completed in 1616. The mosque was designed by the architect Sedefkar Mehmed Agha, who was a student of the renowned architect Mimar Sinan.
- Architectural Style: The Blue Mosque is a masterpiece of Ottoman architecture, combining elements of both classical Ottoman design and Byzantine influence. It features a large central dome flanked by smaller domes, a characteristic of Ottoman mosque architecture.
- Interior Decoration: The interior of the mosque is famous for its exquisite tilework, which gives it the “Blue Mosque” nickname. The walls are adorned with tens of thousands of blue ceramic tiles, intricate calligraphy, and geometric patterns. The high ceilings are decorated with painted designs and arabesques.
 Courtyard and Minarets: The mosque’s courtyard is spacious and features a central fountain for ablution. The mosque has six minarets, a unique feature at the time of its construction. This caused controversy, as the Grand Mosque in Mecca also had six minarets. The issue was resolved by the Ottoman ruler gifting a seventh minaret to the Grand Mosque.
Courtyard and Minarets: The mosque’s courtyard is spacious and features a central fountain for ablution. The mosque has six minarets, a unique feature at the time of its construction. This caused controversy, as the Grand Mosque in Mecca also had six minarets. The issue was resolved by the Ottoman ruler gifting a seventh minaret to the Grand Mosque.- Prayer Hall and Central Dome: The mosque’s prayer hall is characterized by its grandeur and spaciousness. The central dome is supported by four massive piers and is flanked by half-domes on each side, creating a sense of unity and symmetry. The main prayer area can accommodate a large congregation.
- Tourism and Worship: The Blue Mosque remains an active place of worship, hosting daily prayers and Friday congregational prayers. It’s also a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world who come to admire its architecture and historical significance.
- Location: The Blue Mosque is situated in the historic Sultanahmet district of Istanbul, adjacent to another iconic monument, the Hagia Sophia. This area is often referred to as the “Sultanahmet Square” and is a hub of cultural and historical attractions.
- Cultural and Religious Significance: The mosque holds significant cultural and religious importance for both locals and tourists. It stands as a symbol of Ottoman grandeur and architectural innovation, as well as an important site for Islamic worship and cultural heritage.
Overall, the Blue Mosque is a masterpiece of architectural and artistic achievement that reflects the splendor of Ottoman Istanbul and continues to be a cherished landmark in the city’s landscape.